Failed Back Surgery Syndrome (FBSS) presents a complex challenge in the domain of pain management, necessitating a nuanced, multi-pronged approach. Both pharmacological interventions and non-drug therapies come into play, and often require customization to suit individual patient needs. The efficacy of such strategies is a topic of ongoing discussion and research within the medical community. As we explore this intriguing area, we invite you to join us in examining the various aspects of FBSS pain management, from medication options to physical therapy, psychological support, and beyond.
Understanding Failed Back Surgery Syndrome
Grasping the complexity of Failed Back Surgery Syndrome (FBSS) is vital for both patients and healthcare providers. FBSS is a chronic pain condition that occurs when the expected outcome of spine surgery is not achieved, leaving patients battling persistent pain. It’s a complex issue, fraught with diagnostic challenges and deeply personal patient experiences.
One of the significant diagnostic challenges of FBSS is that its symptoms often mimic those of other conditions, making it difficult to isolate and identify. It requires a sophisticated understanding of spine anatomy, surgical procedures, and the myriad ways in which the body can respond to surgical intervention. The diagnostic process can be a lengthy and frustrating one for patients, as they grapple with the uncertainty of their condition and the ongoing pain.
Patient experiences with FBSS are as varied as the individuals themselves. The persistent pain can lead to a cycle of physical discomfort, emotional distress, and social isolation. These experiences underscore the need for a thorough approach to the diagnosis and management of FBSS, one that takes into account the physical symptomatology as well as the psychosocial implications of the condition. Understanding FBSS is a vital first step towards effective pain management.
The Importance of Personalized Pain Management
Recognizing the unique complexities of each patient’s experience with Failed Back Surgery Syndrome (FBSS) is pivotal in formulating a personalized pain management plan. This approach begins with an individualized assessment, taking into account not just the physical symptoms but also the emotional, psychological, and social factors that influence a patient’s experience of pain.
This multifaceted understanding of a patient’s condition allows clinicians to develop tailored interventions that address the specific needs and challenges of each individual. Personalized pain management is not a one-size-fits-all solution but a dynamic process that adapts to the changing needs of the patient.
It involves ongoing communication, reassessment, and adjustments to the plan as necessary. Additionally, it requires a collaborative effort between patients and their healthcare team, fostering a partnership that empowers patients and encourages active participation in their own care.
Exploring Medication Options for FBSS
In the domain of personalized pain management for FBSS, a key facet involves considering the broad spectrum of medication options. These choices range from opioid alternatives and anti-inflammatory medications to more localized treatments like nerve blocks and topical analgesics.
Opioid alternatives, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and acetaminophen, can provide effective pain relief with fewer risks than traditional opioids. Muscle relaxants can also help by reducing muscle spasms often associated with FBSS. For localized pain, nerve blocks or topical analgesics may be suitable options, delivering relief directly to the affected area.
Beyond these, cognitive therapy can complement pain management plans, helping patients better manage the psychological aspects of chronic pain. This therapeutic approach can ameliorate feelings of hopelessness and fear often associated with persistent pain conditions.
For persistent, severe pain, interventional techniques such as epidural steroid injections or spinal cord stimulation might be considered. Always remember that each patient is unique, and a personalized approach to medication management is essential.
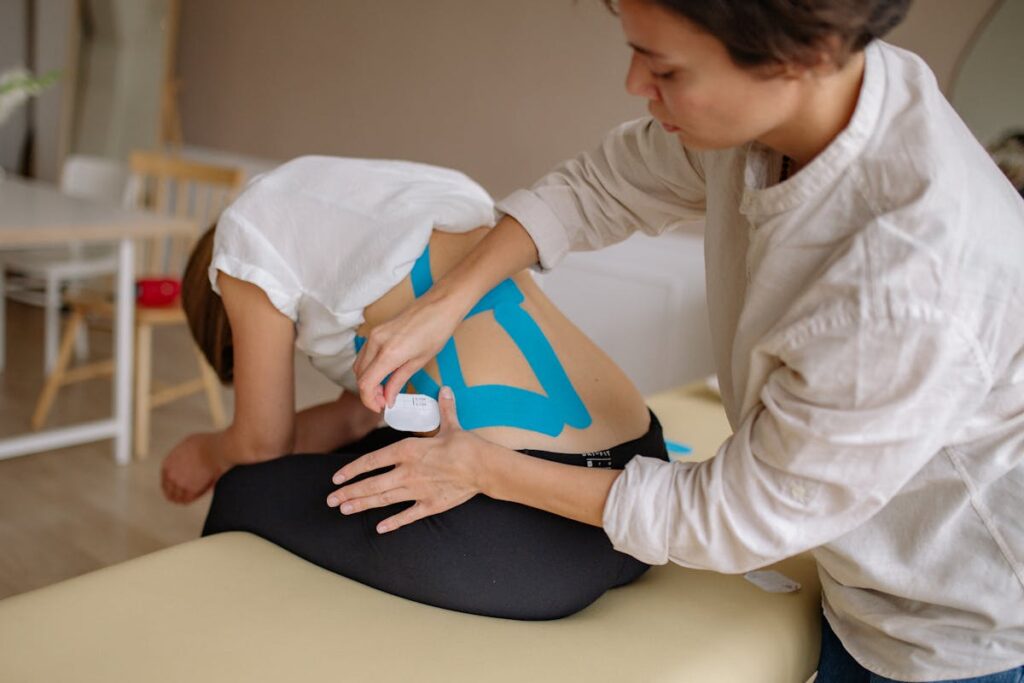
The Role of Physical Therapy in FBSS
In managing Failed Back Surgery Syndrome (FBSS), a significant role is played by physical therapy, which offers non-invasive and often effective solutions. A range of physical therapy techniques can provide relief and improve mobility, while also promoting overall wellness. For individuals experiencing similar pain patterns, exploring targeted sciatica treatments for long-term relief can be beneficial in managing the discomfort that often accompanies FBSS. The subsequent discussion will focus on these techniques, and the potential outcomes patients might expect from such therapeutic intervention.
Physical Therapy Techniques
Physical therapy often steps into the spotlight when it comes to managing Failed Back Surgery Syndrome (FBSS), providing a ray of hope for patients grappling with persistent discomfort. A combination of various physical therapy techniques can considerably alleviate pain, enhance mobility, and improve overall quality of life.
The cornerstone of physical therapy in managing FBSS includes:
- Manual therapy to alleviate pain and enhance joint mobility.
- Exercise prescription involving strength conditioning and mobility exercises tailored to individual needs.
- Aquatic therapy to reduce stress on the spine while providing resistance for strengthening.
- Neuromuscular reeducation and functional training to enhance movement efficiency and reduce strain.
These techniques are often complemented by posture correction and pain modalities, which further assist in managing patient discomfort. Patient education also forms an integral part of physical therapy, empowering patients with knowledge about their condition, self-care techniques, and lifestyle modifications. This integrative approach guarantees a holistic management of FBSS, bringing patients closer to a pain-free life. Through physical therapy, patients can regain control of their lives, redefining their journey with FBSS.
Outcome of Therapy
Often, the outcome of physical therapy in managing FBSS is considerably promising. This is achieved by employing effective rehabilitation strategies that focus not only on the physical, but also on the emotional resilience of patients. Through a multidisciplinary approach, therapists address chronic pain, a common complication of failed back surgeries, and work towards improving the patient’s quality of life.
Surgical complications can adversely affect patient outcomes. However, the efficacy of physical therapy treatments often mitigates these complications. This is enhanced by patient education on self-management techniques, thereby promoting a more active role in their recovery process.
Accessible healthcare is essential for the success of these therapies. With easy healthcare access, patients can adhere to their therapy schedules, leading to more favorable outcomes. On the other hand, barriers to healthcare access may lead to inconsistent therapy sessions, contributing to less than ideal results.

Psychological Support for Chronic Pain
Addressing chronic pain, particularly in cases of Failed Back Surgery Syndrome (FBSS), requires more than just physical remedies; psychological support plays an equally essential role. The enduring discomfort often leads to emotional distress, making patients more susceptible to depression, anxiety, and a diminished quality of life.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a proven method in managing chronic pain. It equips patients with coping mechanisms, helping them to alter negative thought patterns and behaviors linked to their pain.
Emotional resilience is another key aspect of psychological support. Building resilience empowers patients to endure the ongoing physical pain and cope with the emotional toll it takes. It fosters a positive outlook, aiding patients in their journey towards pain management.
The importance of psychological support can be summarized as follows:
- Encourages the development of coping strategies through Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
- Promotes emotional resilience, enabling patients to better manage their pain
- Reduces the risk of mental health issues often associated with chronic pain
- Enhances overall quality of life and patient satisfaction
Thus, treating chronic pain, especially in FBSS cases, should involve a thorough approach that includes rigorous psychological support.
Alternative Therapies for Pain Relief
Although psychological support plays a significant role in managing chronic pain, it is only one aspect of a detailed treatment approach. Other alternative therapies can offer significant relief, complementing traditional pain management methods.
Among these, acupuncture benefits are well-documented, with evidence suggesting it can reduce some types of chronic pain. Similarly, chiropractic adjustments can help realign the spine, potentially easing discomfort. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) is another option, delivering low-voltage electrical currents to the skin to alleviate pain.
Mindfulness meditation can also be beneficial, teaching patients to manage their pain by focusing on the present moment and accepting their physical discomfort. Biofeedback techniques further equip patients to control their body’s responses to pain, enhancing their ability to cope.
Herbal remedies, while not universally accepted, may provide relief for some. Likewise, nutrition therapy can support overall health, potentially influencing pain levels. Aromatherapy practices, using essential oils to stimulate the senses, can promote relaxation and alleviate stress, a common aggravator of chronic pain.
It’s important to remember that alternative therapies should be part of a thorough pain management plan, tailored to each patient’s unique needs and preferences.
Lifestyle Modifications for Managing FBSS
Maneuvering the complex landscape of Failed Back Surgery Syndrome (FBSS) requires more than medical interventions and alternative therapies. Incorporating thorough lifestyle modifications can have a significant impact on managing FBSS. These modifications are not a one-size-fits-all solution, but rather, a highly personalized approach that addresses the unique needs and circumstances of each individual.
A holistic approach to managing FBSS can include:
- Dietary changes and hydration strategies: Eating a well-balanced diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding inflammatory foods can help mitigate FBSS symptoms.
- Exercise routines and activity pacing: Regular, gentle exercise can improve physical condition, while pacing activities can prevent overexertion.
- Sleep hygiene and stress reduction: Establishing a regular sleep schedule and using mindfulness practices can enhance restorative sleep and reduce stress levels.
- Ergonomic adjustments and hobby engagement: Adjusting workspaces for comfort and engaging in hobbies can improve physical well-being and mental health.
Furthermore, leveraging social support can be instrumental in managing FBSS. Loved ones can provide emotional support, assist with daily tasks, and help guarantee adherence to these lifestyle modifications. By integrating these changes into their daily lives, individuals with FBSS can improve their quality of life and reduce their reliance on medical interventions.
Coping Strategies for Daily Life
Living with Failed Back Surgery Syndrome (FBSS) often presents a labyrinth of challenges, demanding not just physical resilience but also psychological fortitude. The constant discomfort can become a significant barrier in daily routine, making it essential to develop coping strategies that not only manage pain but also help in improving overall quality of life. For individuals facing the aftermath of an unsuccessful surgery, exploring the next steps after unsuccessful back surgery can provide crucial insights and guidance on managing the situation effectively.
Incorporating mindfulness practices can be an essential part of your coping arsenal. These practices involve focusing your mind on the present moment, which can help reduce the perception of pain. Techniques such as deep breathing, guided imagery, and progressive muscle relaxation can promote relaxation and help you deal with pain more effectively.
Additionally, stress reduction plays a pivotal role in managing FBSS. High stress levels can exacerbate pain and hinder recovery. Techniques like yoga, tai chi, and other forms of gentle exercise can be beneficial in reducing stress levels. These can also improve physical strength and flexibility, thereby supporting better body movements.
Lastly, it is imperative to maintain a positive attitude. This may be challenging, but remember, you are not alone. Seek support from healthcare professionals, support groups, family, and friends. With the right strategies and support, living with FBSS can become more manageable.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Potential Surgical Complications Leading to Failed Back Surgery Syndrome?
Possible surgical risks leading to Failed Back Surgery Syndrome include improper preoperative patient selection, nerve damage, infection, spinal instability, and hardware malfunction. These complications can lead to persistent or worsening postoperative pain.
How Does FBSS Affect Sleep Patterns and Overall Quality of Life?
Failed Back Surgery Syndrome (FBSS) often results in significant sleep disturbances due to chronic pain, thereby negatively impacting overall quality of life. An effective quality assessment is essential to determine appropriate interventions for these patients.
Can Failed Back Surgery Syndrome Be Completely Cured With Subsequent Surgeries?
While subsequent surgeries may offer some relief, Failed Back Surgery Syndrome cannot be completely cured. Ideal treatment often involves surgical alternatives, alongside thorough pain management strategies, to improve patients’ quality of life.
How Does Weight and Diet Influence the Severity of FBSS Symptoms?
Weight and diet greatly influence FBSS symptoms. Obesity intensifies strain on the spine, exacerbating pain. Adopting nutrition strategies, like a balanced diet, can reduce weight and consequently, mitigate the severity of FBSS symptoms.
Are There Any Specific Exercises to Avoid When Diagnosed With Failed Back Surgery Syndrome?
Patients with Failed Back Surgery Syndrome should generally avoid high-impact and heavy lifting exercises. Instead, focus should be on low-impact strength training and flexibility exercises, under the guidance of a trained physical therapist.